


Sunflower Autumn Beauty (treated seed)
Branching, long-stemmed sunflower with solid colour and bicolour flowers in rich earthy tones. With a long flowering period the branching habit gives rise to lots of side flowers of varying sizes. Great as a background plant in the border or cut in bouquets. Also attractive to pollinators and bees.
Treated Seed: This seed is treated in order to meet biosecurity import regulations. Use caution when handling and do not use for food, feed or oil.
Botanical Name
Lifecycle
Sowing Time
Growing Guidance
Preferred Site
Preferred Growing Method
Soil Temperature for Optimum Germination
Days to Germination
Days to Maturity
Plant Height
Sowing Time
Sowing time refers to the optimum time for sowing seed of a variety to encourage strong and vigorous growth. Whilst some varieties may be able to be sown outside the range suggested, they will generally perform best when sown in the approximate seasonal ranges provided.
A lot of seeds need consistent warmth to help them germinate. The best way to achieve this is to sow at the right time. By sowing in season when the conditions are optimum for seed germination you are increasing your chances of success. Slight bottom heat, approximately 20°C, can speed germination of many varieties.
To reference the best sowing times for a variety, we use sow numbers as detailed here:
- Early Spring
- Late Spring & Early Summer
- Late Summer & Early Autumn
Growing Method
DIRECT SOW
- Soil Preparation: Turn over garden soil with spade or fork. A loose soil enriched with moderate amounts of organic matter or fertiliser to supply nutrients is best. Add any other conditioners such as peat moss, compost or sand etc., if not added the previous autumn. Break up the clods of earth and rake to produce a fine surface.
- Sowing: Sow seed evenly in rows as directed. Lightly cover the seed with soil, a sieve may be useful. Depth should be no more than twice the diameter of the seed. In the case of very fine seed no covering is needed. Use the palm of your hand to press down on the soil to create a firm surface.
- Watering: Water the soil either by a watering can or hose using a very fine spray until the surface appears damp.
- Thinning: When seedlings are about 6cm high or have developed their first true leaves (recognisable as those of the sown species) the row should be thinned out to the plant’s required spacing.
- Moisture Management: Keep soil moist but not drenched to ensure germination and rapid growth. When watering overhead, water earlier in the day to prevent having wet leaves overnight when the conditions are not as suitable for drying promoting disease development. The soil should appear dark and not brown to indicate appropriate moisture levels.
General Definitions
Annual
A plant that completes its entire life cycle (germinates, grows a plant, flowers, produces seed, dies) in one season. It may self-sow, thereby giving the impression of being perennial. Most annuals will flower 60 to 75 days from sowing.
Hardy Annual
An annual that does not need to be germinated indoors but can be sown direct into its growing position in the garden in spring and is tolerant of frost.
Tender Annual
An annual that is frost tender and can be germinated indoors. Sowing direct or planting outdoors must not occur until all danger of frost has passed (also known as a Half-Hardy Annual).
Biennial
A plant that completes its entire life cycle in two years - growing in the first, reproducing and dying in the second. Typically, but not always, producing flowers only in the second year.
Perennial
A plant that can live for more than two years, surviving the winter and flowering each year from the second season. Perennials may flower within 90 days of sowing in their first season but will more typically flower in their second
season.
Hardy Perennial
A perennial that is frost-tolerant.
Tender Perennial
A perennial that is frost tender.
Hardy
A plant that will survive frost.
Tender
A plant that will not survive frost.
Bolting
Going to seed. Premature formation of a seed stalk, may be due to plant stress.
Botanical Name
The formal scientific name conforming to the International Code of Nomenclature for plants. Identifies the genus and species to which the plant belongs useful in distinguishing plants uniquely.
Cotyledon
The seed leaves or first leaves that emerge from a germinated seed, different in form from the later true leaves.
True Leaves
The leaves that emerge after the cotyledons which are indicative of the true form
of the plant’s leaves.
Determinate
Growth stopped by development of terminal flower buds. A dwarf/bush variety which sets fruit in a concentrated period.
Indeterminate
Growth continuing indefinitely when leaf buds form at the tip of the growth. These varieties need to be staked and continue to set fruit until frost.
Heirloom
A variety that is older than two generations (50 years). Can also be referred to as “Heritage” and is always an open pollinated variety selected for garden performance (flavour, long harvest).
Hybrid
A plant resulting from a cross between two parent plants to give a genetically superior plant i.e. improved disease resistance, better vigour, more uniform harvest. Normally, seed saved from hybrids does not grow true to type.
F1 - The first generation of such a cross. Denoted in the name of the variety.
F2 - The second generation of such a cross etc.
Open Pollinated
Natural cross between plants of the same variety. Refers to non-hybrid seeds or plants.
NPK
Basic nutrient needs of plants:
Nitrogen
(N) - for green growth, healthy soil and microbial activity
Phosphorus
(P) - for flower, fruit and seed production; vigorous roots and disease resistance
Potassium
(K) - essential for building plant tissue (important for young plants) and the
quality and size of fruit.
pH A measurement for the acidity/alkalinity of soil, needed for nutrientavailability and microbial activity.
Scarification
Thepractice of scratching or notching the seed coat to assist germination. Usually
applies to hard coated seed.
Stratification
Chilling seeds to promote germination by breaking dormancy.
Viability
The ability of seeds to germinate.
Vigour
The speed and the strength
of the plant to establish well.
Delivery
Courier delivery by NZ Post.
Delivery available only to valid New Zealand
addresses.
The appropriate delivery charge will be applied at checkout.
Delivery charges are subject to change without notice.
You can track the status of your shipment via the link provided in your order confirmation email or by logging into your account online.
Click n Collect
Seed can only be collected from our warehouse at 189 Wharawhara Rd, Katikati
Select Click n Collect at the checkout
Click n Collect does not apply for collection at any Kings Seeds stockists nationwide.
Returns
Seed or Products can only be returned with authorisation from Kings Seeds.
Any request for the return of Seed or Products must be made within 14 days of delivery to info@kingsseeds.co.nz
Returned Seed or Products will only be accepted if unopened and in the same condition as when supplied and a record of
your purchase can be found
The Customer shall pay all costs in relation to return of the Seed or Products unless it is deemed a warranty issue.
Please see our Terms & Conditions of Sale for further information on our Returns Policy.
Share
Recently Viewed
Related Categories
@kingsseedsnz
Follow us on Instagram
Agastache Fragrant Carpet
Colourful blend of compact agastache that flower the first season in shades of pink, ro

Antirrhinum Lucky Lips
Spectacular tall snapdragon with distinctive contrasting white flowers with carmine-col

Antirrhinum Snowflake
Pure white snapdragon for the summer garden border and for cutting. The upright strong

Antirrhinum Twilight Mix
Dwarf antirrhinum in various shades of rose, pink and yellow with contrasting dark foli

Artichoke Imperial Star F1
High quality green globes in the first season from seed. Typically 6-8 mature buds will

Asperula Sweet Blue Woodruff
Beautiful annual covered with lavender-blue, tubular flowers from early to late summer.

Beetroot Chioggia
Originating from Chioggia in Italy, these fascinating beets produce red, globe-shaped r

Briza Quaking Grass
Ornamental grass with graceful paper lantern-like flower heads that are white, tinged w

Brussels Sprouts Long Island
Vertical plants perfect for inter-planting. Formation of sprouts is stimulated by pulli

Brussels Sprouts Magenta
A novelty purple/red Brussels sprout, it matures over a long period with colour develo

Cabbage Chinese Mini Gold F1
Fast growing, mini Kimchi cabbage with a golden yellow interior and a sweet, crunchy fl

Cabbage Verona Purple Savoy
Popular European savoy cabbage with a purple blush to its leaves that's enhanced with c

Candytuft Flash Mix
Mound-shaped plants form a blanket of colour including shades of lilac, purple, white,

Capsicum California Wonder Golden
Highly regarded heirloom capsicum, noted for its adaptability and reliability. Sweet an

Capsicum Golden Bell F1 (treated seed)
High quality hybrid capsicum ripening to a glossy gold at maturity. The uniform 180g fr

Carrot Kuroda Improved
A bright orange kuroda carrot with wide shoulders tapering to a blunt point. Medium lon
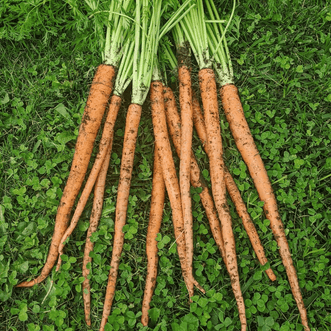
Carrot Nagai (treated seed)
Super long heirloom carrot from Japan, can grow to over 60cm yet still be sweet and cri

Carthamus Zanzibar (treated seed)
Also known as safflower, this beautiful flower can be used for fresh or dry cut-flower

Cauliflower Giant of Naples
Impressive cauliflower for gardeners with space. With a curd size of 1.6 to 1.8kg, the

Chilli Cherry
Cherry chillies typically have a Scoville rating of about 2,500 to 5,000. These chillie

Cleome Mix
Also known as spider flowers, featuring scented, spidery blooms atop sturdy stems, addi

Cucumber Longfellow
Heirloom cucumber bred in 1927 and named after the poet Henry Longfellow. An extra long

Cucumber Pick A Bushel F1
Be prepared to pick a lot of gherkin-size pickling cucumbers from these compact but vig

Dianthus Clove Pinks
A pretty mix of carnations in shades of pink from deep rose to pale pink and white, wit

Echinacea White Swan
A striking echinacea producing lime-green/cream blooms that mature to white with distin

Echium Blue Bedder
This fabulous bee plant can play a vital role in your garden ecosystem by attracting po

Eggplant Dok F1
High yielding eggplant with long violet-pink fruit, popular in Asian cuisine. Quick to

Eggplant Florence Round Purple
A beautiful and unusual eggplant with oblong to round fruits in shades of rich lavender

Fennel Bronze Smokey
A perennial herb that is highly versatile with striking bronze/green foliage that can b

Fennel Finale
Tasty, reliable and bolt tolerant for year round sowing. Firm flattened bulbs that are

Gerbera Transvaal Daisies
Brightly coloured mix of clump forming gerberas, also known as the Barbarton daisy. Nat

Geum Mrs Bradshaw
A striking plant known for its vibrant semi-double, scarlet-red blooms that are great a

Gourd Mini Monster Mix F1
Blend of lumpy, bumpy, bi-coloured, winged and warted miniature gourds. Bland and inedi

Hyacinth Bean Vine Silver Moon
Spectacular selection with silvery-white flowers. A fast-growing climber for covering w

Kale Noble
Known for its remarkable resilience and fast growth, a gentle frost not only enhances i

Kale Ornamental Pick 'n' Mix F1
Colourful and frilly leaves pretty in winter gardens and a unique element for floral wo

Komatsuna Red Leaf F1
Tasty purple-red mustard spinach. Excellent addition to baby leaf salads and lightly sa

Leek Lungo della Riviera
Tall and slender gourmet Mediterranean leek that's great for tasty and tender baby leek

Lettuce Coastline
Frillice type lettuce with serrated/frilled leaf margins and crisp, mid-green leaves. O

Lettuce Crisp Mint
Attractive mint-green upright Cos/Romaine lettuce with crisp, sweet-tasting slightly ru

Lettuce Little Caesar
A dark-green, mini cos that is grown for cos hearts or small leaves for making salads.

Lettuce Perella Rougette Montpellier
A red butterhead variety, this Italian heirloom produces compact heads of green with bl

Lettuce Rouge d'Hiver
150 year old European heirloom has broad flat leaves ranging in colour from green to br

Lettuce Tennis Ball
Heirloom mini lettuce from the 17 century that still performs today. Given the compact

Lettuce Tom Thumb
An English Heirloom that combines taste and space-saving. Ideal for small gardens and c

Liatris Florist Violet
A fantastic cut flower with its long vase life and striking vertical blooms that add he

Linaria Licilia Peach
A delicate, airy plant with flowers that look just like baby snapdragons, bi-coloured -

Linaria Licilia Red
A delicate, airy plant with bright-red flowers that look just like baby snapdragons. Pl

Lupin Avalune Blue
Sweetly scented lupin with whorls of deep lavender-blue florets. Suitable for pots, bor
Your Cart is Empty
Know what you’re looking for?
In a hurry? Know exactly what you want? You can enter the product codes here and proceed straight through the Checkout.
Use Quick CheckoutEarn two FREE Packets
You are just $40.00 away from earning two FREE packets.
Purchase value excludes gift cards purchased & delivery charges.
You have reached the maximum FREE bonus packets
Loading...
Subtotal
NZ $0.00
Taxes and shipping calculated at checkout
You May Like
Cauliflower Giant of Naples
250 seeds
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.

